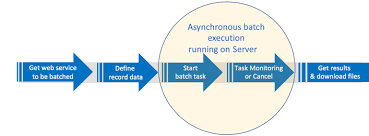
In this article, we’ll be discussing Asynchronous Batch Apex, which is a crucial topic in Salesforce development. But first, let’s understand the difference between synchronous and asynchronous apex.
Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Apex
Synchronous Apex runs on a single thread, so only one operation or program will execute at a time. On the other hand, Asynchronous Apex is multi-threaded, which means programs can run simultaneously. Additionally, Asynchronous Apex is non-blocking, so it can send multiple requests to a server.
Example of Synchronous Batch Class
Here’s an example of a Synchronous Batch Class in Salesforce:
global class EmailMessageCleanupBatch implements Database.Batchable<SObject> {
global Database.QueryLocator start(Database.BatchableContext bc) {
String query = 'SELECT Id, CreatedDate FROM EmailMessage WHERE CreatedDate < LAST_N_DAYS:365 limit 1';
return Database.getQueryLocator(query);
}
global void execute(Database.BatchableContext bc, List<EmailMessage> Emaillist) {
List<EmailMessage> ToBeDeletedEmailMessage = new List<EmailMessage>();
for(EmailMessage eml : Emaillist) {
ToBeDeletedEmailMessage.add(eml);
}
if(ToBeDeletedEmailMessage.size() > 0) {
delete ToBeDeletedEmailMessage;
}
}
global void finish(Database.BatchableContext bc) {}
}
Executing the Batch Class
To execute the above batch class, we need to run the following code snippet:
EmailMessageCleanupBatch batchclass = new EmailMessageCleanupBatch();
Database.executeBatch(batchclass);
Testing the Batch Class
Here's an example of a test class for the batch class above:
@isTest
public class EmailMessageCleanupBatchTest {
@testSetup
public static void createTestData() {
// create email messages older than 365 days
List<EmailMessage> emList = new List<EmailMessage>();
Date olderThan365days = Date.today().addDays(-365);
EmailMessage em = new EmailMessage();
em.Subject = 'Test Email';
em.TextBody = 'Test Email Body';
em.ToAddress = 'test@test.com';
em.CreatedDate = olderThan365days;
emList.add(em);
insert emList;
}
@isTest
static void testEmailMessageCleanupBatch() {
Test.startTest();
// execute batch
EmailMessageCleanupBatch batchclass = new EmailMessageCleanupBatch();
Database.executeBatch(batchclass);
Test.stopTest();
// assert that all email messages older than 365 days have been deleted
List<EmailMessage> emList = [SELECT Id, CreatedDate FROM EmailMessage WHERE CreatedDate < LAST_N_DAYS:365];
System.assertEquals(0, emList.size());
}
}
Conclusion
Asynchronous Batch Apex is an essential concept in Salesforce development. It allows developers to process large volumes of data asynchronously, without blocking the user interface. By understanding the difference between synchronous and asynchronous apex, you can choose the appropriate approach for your use case.
Hits: 0